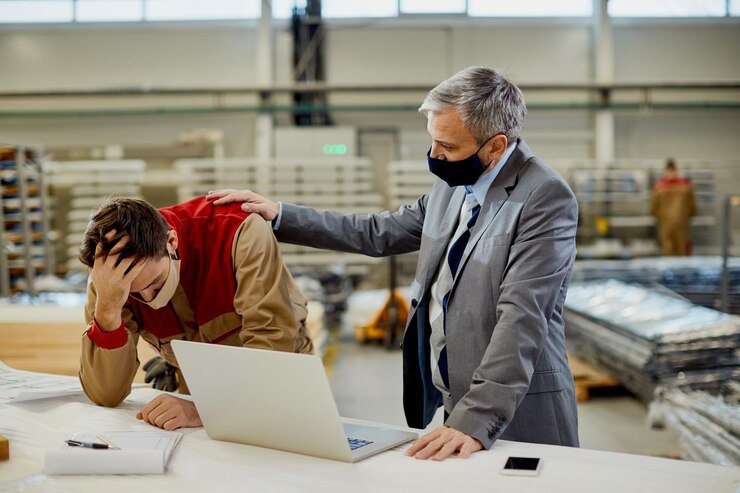
Introduction
The relationship between business owners and workers has been marked by moments of tension throughout history, shaped by economic structures, social dynamics, and competing interests. While business owners strive to maximize profitability and operational efficiency, workers often advocate for fair wages, reasonable working conditions, and job security. This inherent conflict of priorities has led to significant tension, particularly during periods of economic upheaval or rapid industrialization. Understanding the root causes of this tension is essential for fostering more harmonious and productive workplace relationships.
1. Diverging Priorities: Profit vs. Welfare
Why was there tension between business owners and workers lies the fundamental conflict between profit maximization and employee welfare. Business owners are primarily focused on reducing costs, increasing productivity, and maximizing returns for stakeholders. This often involves measures such as streamlining operations, implementing automation, or limiting wage increases. Workers, on the other hand, seek fair compensation, benefits, and safe working conditions. The pressure to balance these priorities frequently leads to disputes, as workers feel their contributions are undervalued while business owners contend with the challenges of maintaining competitiveness.
2. Historical Context: The Industrial Revolution and Beyond
The industrial revolution marked a pivotal moment in the history of labor relations, as mass production and factory systems transformed the workforce. Business owners benefited from economies of scale, but the shift to mechanized labor often came at the expense of workers’ rights and well-being. Long hours, unsafe conditions, and minimal pay were common, leading to widespread dissatisfaction and the rise of labor movements. Strikes and protests became tools for workers to demand change, further intensifying tensions. Even in modern times, echoes of these historical conflicts persist in industries where worker protections are limited or poorly enforced.
3. The Role of Labor Unions
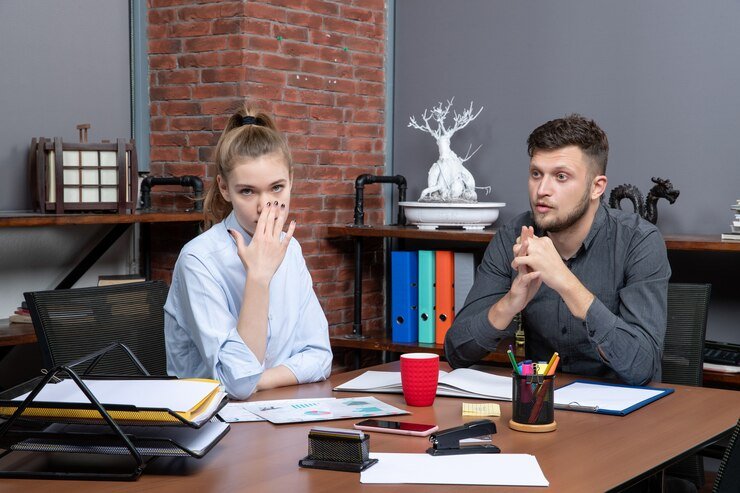

Labor unions have played a critical role in addressing the imbalance of power between business owners and workers, advocating for collective bargaining and better workplace conditions. While unions have been instrumental in securing higher wages and improved benefits, their efforts have sometimes been met with resistance from business owners. Employers often perceive unions as a threat to profitability and operational control, leading to efforts to undermine unionization or negotiate minimal concessions. This adversarial relationship underscores the ongoing struggle to reconcile the interests of workers and employers within a capitalist framework.
4. Economic Pressures and Globalization
Economic pressures, such as market competition and globalization, have further exacerbated tensions between business owners and workers. Globalization, in particular, has introduced new challenges, as businesses seek to remain competitive by outsourcing labor to regions with lower costs. While this strategy benefits business owners, it often results in job losses and wage stagnation for domestic workers. Additionally, the rise of gig and freelance economies has created new forms of tension, as workers in these sectors often lack the stability and benefits traditionally associated with full-time employment.
5. Technological Advancements and Workplace Dynamics
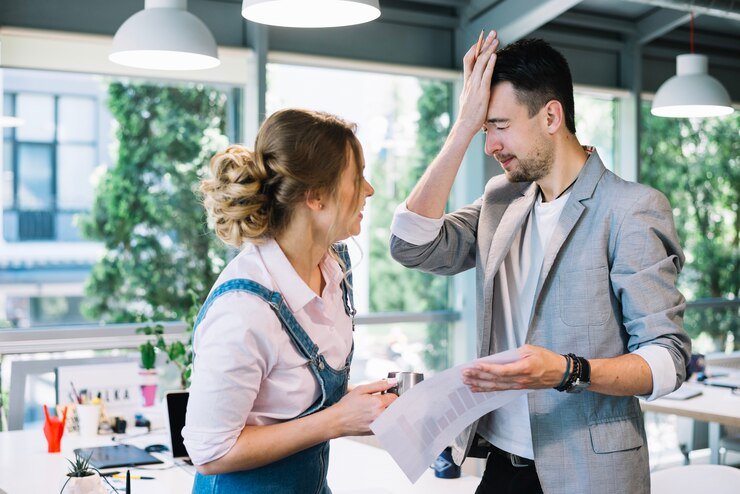

Technological advancements have also contributed to shifting workplace dynamics and tensions. Automation and artificial intelligence have enabled businesses to reduce reliance on human labor, raising concerns among workers about job displacement and the future of work. While technology can improve efficiency and profitability, it also necessitates a reevaluation of skills and workforce roles, creating uncertainty and resistance among employees. The challenge for business owners lies in balancing the adoption of new technologies with the need to invest in workforce development and retraining.
6. Cultural and Generational Shifts
Cultural and generational shifts have introduced new dimensions to the tension between business owners and workers. Younger generations often prioritize work-life balance, ethical practices, and corporate social responsibility, challenging traditional business models focused solely on profitability. These changing expectations require business owners to adapt their strategies to attract and retain talent, fostering an environment that aligns with modern values. However, this transition is not always seamless, leading to friction as businesses navigate evolving cultural norms.
7. Strategies for Bridging the Gap
To mitigate tension and build stronger relationships, business owners and workers must engage in open dialogue and collaboration. Emphasizing transparency, fairness, and mutual respect can help bridge the gap between competing interests. Implementing policies that prioritize employee well-being, such as flexible work arrangements, profit-sharing programs, and professional development opportunities, demonstrates a commitment to creating a more equitable workplace. Additionally, fostering a culture of inclusivity and recognizing the contributions of workers can pave the way for more harmonious labor relations.
Conclusion
The tension between business owners and workers is a reflection of the broader complexities of economic systems and societal structures. By fostering collaboration and prioritizing the shared goals of productivity and well-being, businesses and workers can move toward a more balanced and sustainable relationship that benefits all stakeholders.